How to Optimize Your Network with EIGRP Stub Router
Introduction
The EIGRP stub router is a feature of the EIGRP routing protocol through which we limit the number of routes from being advertisement. Moreover, It is also a helpful feature for EIGRP Stuck in active state when EIGRP queries its neighbors for its failed route. The router will send a multicast query to all of its neighbors.
EIGRP stub router
It helps in EIGRP stuck in an active state. Suppose you want that the multicast query doesn’t go beyond R2. Then we will make R2 a stub router. Due to this, it will not send this query beyond R2. It will stop this query at R2.
In the below topology diagram for this lab,. If the R1 Loopback interface is suddenly down, then R1 will query to find an alternative path to this Loopback interface. It will send a multicast message to its neighbor, R2. R2 will then pass this multicast further to its neighbor. The R3 and R4 will send a reply to R2 that this route is reaching us through you. Similarly, R2 has gotten this failed route through R1. Due to this, it replied to R1’s query for not finding a feasible successor to the failed route.
After configuring R2 as a stub router, it will send its stub information to R1 in a hello message. So, R1 will never send a query message to the R2 (stub router). R1 will send only an update message, but it will not send a query message.
The second scenario of making a router a stub is to stop the advertisement of routes. Stub is a new feature in the EIGRP Protocol. It stops the advertisement of routes from being an advertisement, reducing the routing table’s size. EIGRP stub works on the hub and spoke environment. We don’t configure stub configuration on the hub routers, but we do it on spoke routers.
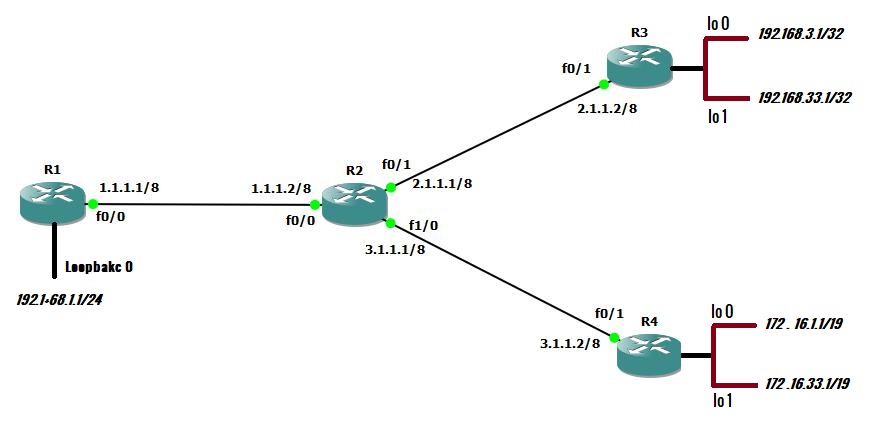
Lab topology for EIGRP stub router
Our lab topology for the EIGRP stub router consists of four routers, as shown in the above diagram. I use the GNS3 software for this lab. Configure all the IP addresses as shown in the diagram. Run EIGRP with autonomous system 1 on all four routers. Moreover, configure R2 as an EIGRP stub router.
Configure R1 and R2 in their basic configuration and run EIGRP with AS number 1.
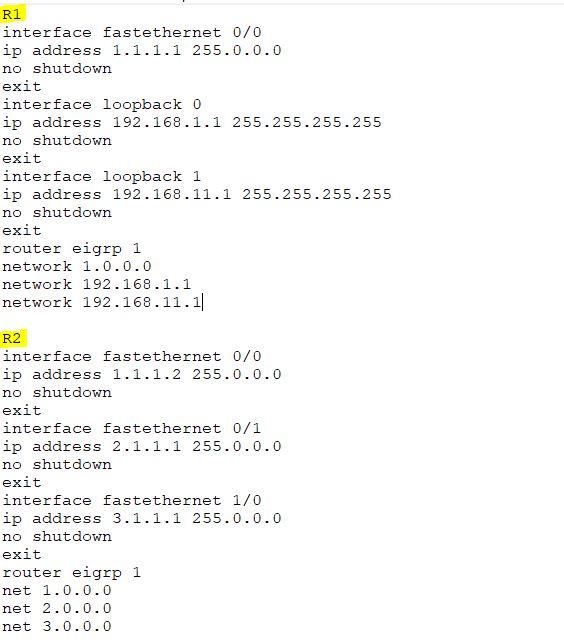
Similarly, configure R3 and R4
Check the routing table of R1 before running the EIGRP stub on R2.
Ping R3 and R4 from R1

Check the neighbors status on R2
Now run the EIGRP stub command on R2

Now, check the routing table of R1
Check the neighbors after configuring the stub command on R2.

Suppose, you want to allow some routes through R2 because all the routes are reaching R2, but R2 then stops at R2. So, we will allow R3’s loopback interface through R2 via leak-map. We will implement a leak-map command through a route map. The required configurations are below in the screenshot.
Allowing Specific Routes from R3 via Leak-Map on R2
The following configuration will be used for the leak-map process on R2.
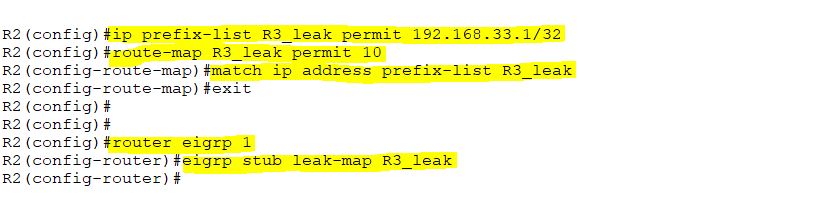
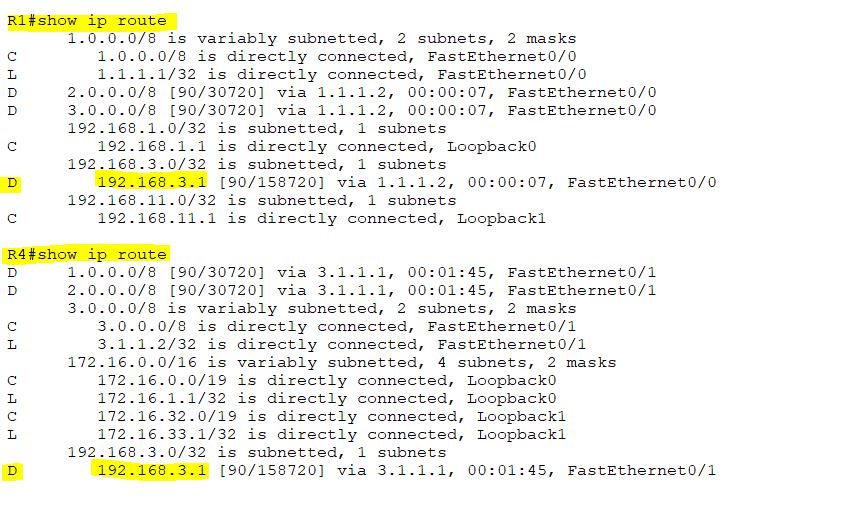
To verify, R3’s loopback interface is at R1 and R4.
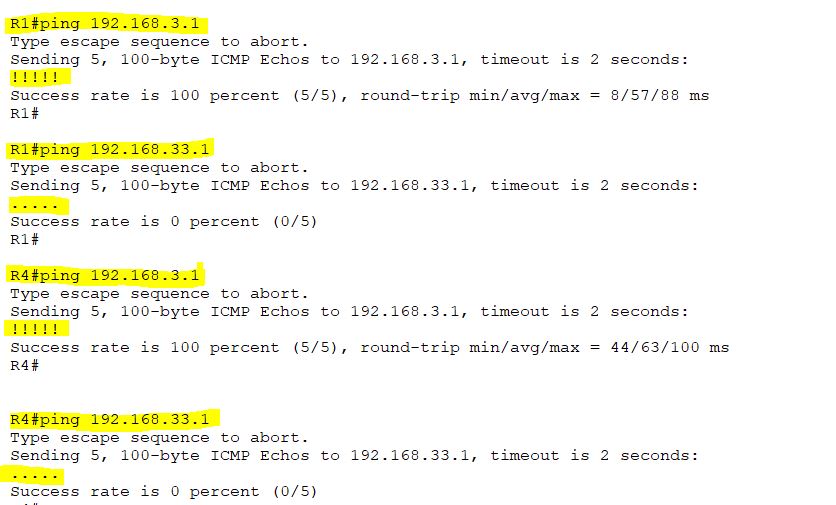
Now check connectivity between R1, R4, and R3’s loopback interface via the ping command.
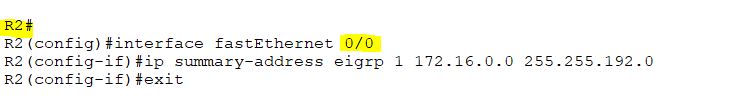
Enabling Summary Route on R2
As we saw in an early configuration, the EIGRP stub command allows only connected and summary routes. We examined connected routes,, but didn’t examine summary routes. Because the connected route is reaching other routers, there is no summary route. So we are going to configure the EIGRP summary route on R2, so R1 will also receive the summary routes of R4’s loopback interfaces, which are 172.16.1.1/19, and 172.16.33.1/19. The summary route for both interfaces is 172.16.0.0/18. So, we will apply it at R2. We are sending summary routes towards R1.
Check the routing tables for R1 and R3. R1 will have a summary route of 172.16.0.0/18, while R3 will not. Because, we send the summary route toward R1, but not toward R3.
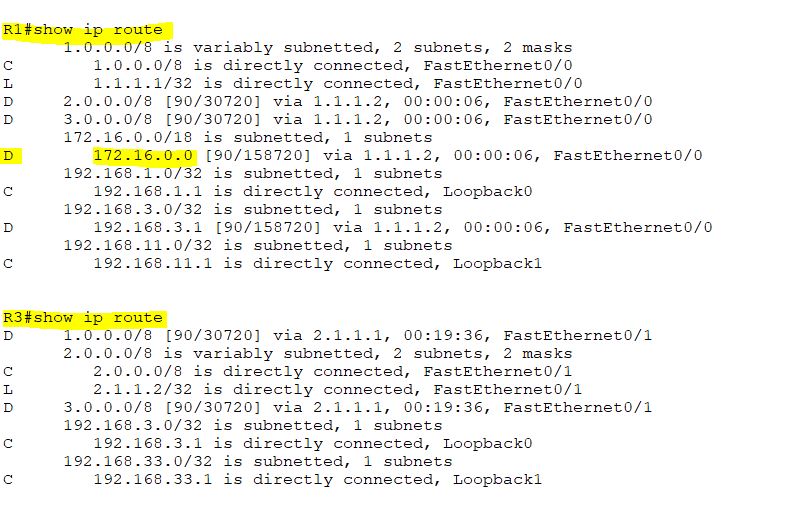
EIGRP stub receive-only command
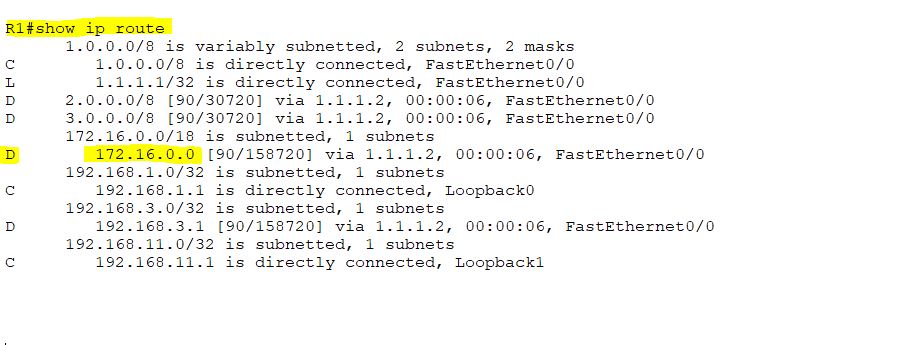
At the last, we will configure the EIGRP receive-only command on R3. After configuring this command on R3, no routes will be advertised to R2. Before, configuring this command on R3, first check R1’s routing table.
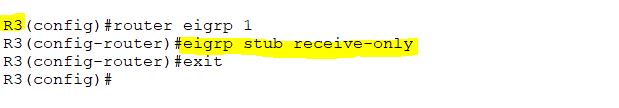
Now, configure EIGRP stub receive-only on R3.
Now check the routing table of R1
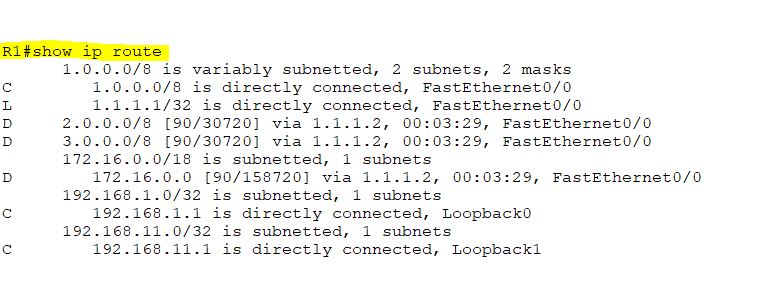
The loopback 0 interface is not reaching R1 now.