How to Understand EIGRP Stuck in Active State
Introduction
There are two types of router states in EIGRP, which are installed in a router’s routing table. The first one is passive, and the 2nd is active. The passive state is considered the best, while the active state is considered harmful. The passive state indicates the route is reachable, while the passive state represents the failed route. When a router goes down, it starts to query its neighbor for an alternative path. As long as the route waits for acknowledgment from its neighbor, it will place the failed route in an active state. That’s why it is called ” EIGRP stuck in an active state.”
EIGRP Stuck in Active State Lab Topology
We will use the following topology to understand EIGRP stuck in an active state.
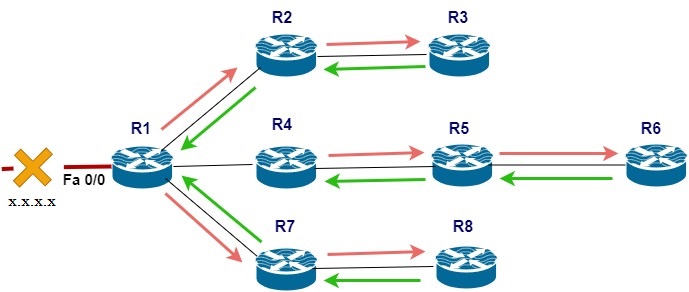
The FastEthernet 0/0 of R1 is installed in the routing table of R1. As it is connected or there is communication between this interface and the router R1. So, it will shown as by the letter “P,” which is passive`.
Suppose R1’s FastEthernet 0/0 has been down due to some reason. R1 will start to generate its query message to all its neighbors. This query message aims to find any alternate or feasible successor path to the failed route.
When the query message reaches R2, then R2 will check this query in its routing table as the x.x.x.x route was reached to R2 via R1. R2 will apply the split-horizon rule by stating that the failed route arrived at me through R1. So, it will not return the received query to the R1, But it will send it to its neighbor R3.
In the same way, R1 will also send the same query to R4 and R7. Consequently, R4 and R7 will pass this query on to their connected neighbors. And at the last, it will propagate throughout the topology.
As long as R1 finds a feasible successor to the failed route. Route x.x.x.x will remain in R1, in the active state during this time, hoping the neighbor router will find any feasible successor for i. That’s why it is called a “Stuck in Active” state.
When all the routers send replies (acknowledgments) back to R1, there is no feasible successor to the failed route, and then the router R1 will remove its entry from its routing table.
The bad face of EIGRP
The default timer for the EIGRP query message is 3 minutes. Suppose there is a slow link or a congested link between R5 and R6. At the same time, R6 doesn’t reply to the R5 within the specified time, which is 3 minutes. Then, R5 will start to break its relationship with R6 by refreshing its neighborship. The purpose of refreshing its neighborship with R6 is to confirm its neighborship. It will re-establish its relationship with R6.
In the same way, as the query message has reached R5 via R4, R4 will also refresh its neighborship with R5, and R1 will re-establish its neighborship with R4. At a glance, there will be a greater breakage in the whole topology.
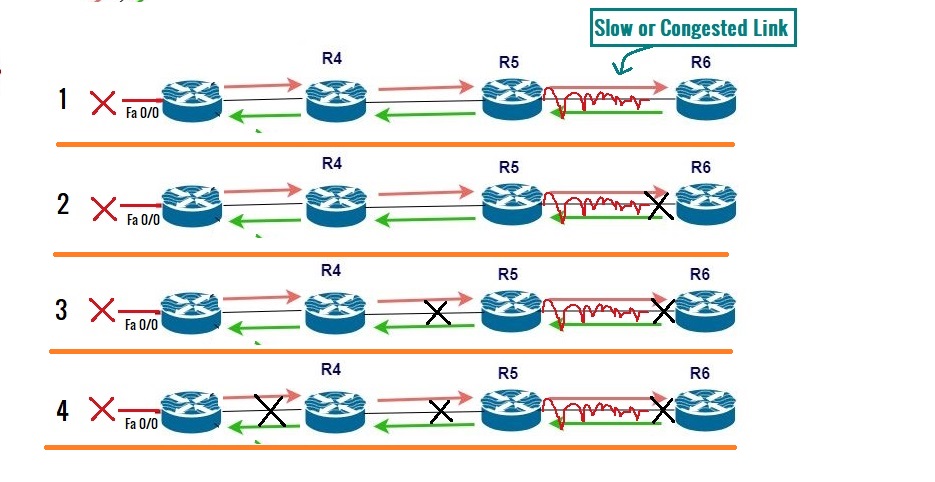
First, R5 will break neighborship with R6, R4 with R5, and at last R1 will break the relationship with R4.
Causes of EIGRP Stuck In Active State
1) Network congestion
Network congestion creates delays in the computer network that cause query messages to have difficulty reaching other routers.
2) Configuration errors
Sometimes, queries don’t reach the destination due to a router being misconfigured.
3) Unreachable Neighbors
When a neighbor is down, due to some reason, queries do not reach their destination.
4) Large EIGRP Network
When the network is very large, it takes time for queries to arrive and get their reply, and sometimes this time exceeds the EIGRP.
5) Hardware/software failures
Sometimes, routers don’t respond due to bad routers or outdated software.
Preventing EIGRP SIA
1) Design Efficient Network Topology
You should ignore complex and overlay networks, as this can cause problems in propagating queries.
2) Optimize EIGRP Timers
You should be very careful when setting the timer.
3) Monitor and Manage Traffic
Ensure that the network segment is not overloaded and that the bandwidth allocated should be sufficient for EIGRP.
4) Maintain Neighbor Stability
You must use a reliable link and hardware to establish neighbor-to-neighbor end adjacency so that neighbors do not go down repeatedly.
5) Use EIGRP Stub
Finally, the most important thing is the EIGRP Stub Router – with this help, we prevent EIGRP Queries from propagating further.