Important types of computer networking devices?
There are many types of devices, which are used in the computer networking industry. We use some devices for small offices or homes. Similarly, we used some devices for medium to large networks. Some devices are obsolete like bridge, hub, etc while some devices have made a modification in it that performs its basic functions as well as some other functions as well. Here, we are going to discuss some computer networking devices, which are below:
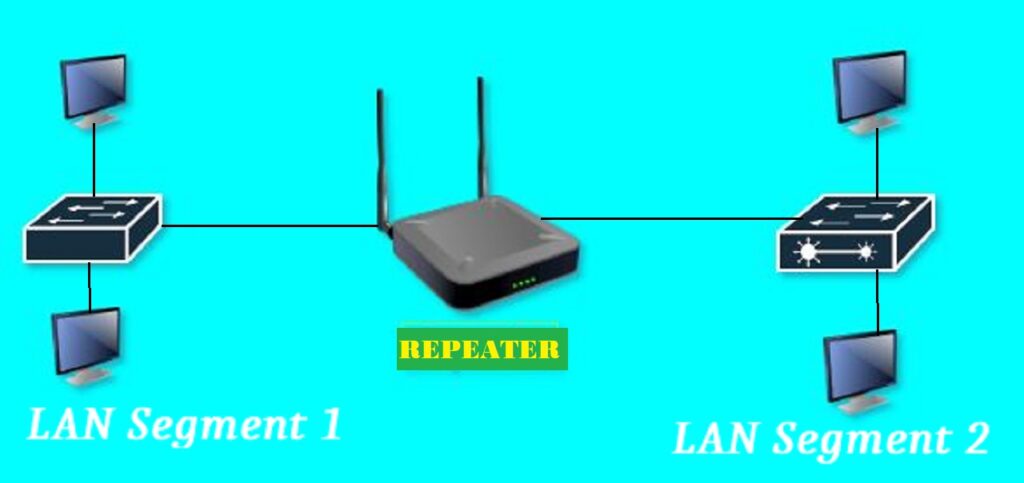
01):- Repeater
A repeater is an important type of computer networking device that receives signals and then retransmits the weak signal to a higher level to forward it. It works at layer one of the OSI Model. Analog repeaters only amplify the signal i.e. it doesn’t filter impurities in the signal, while digital repeaters first filter the noise in the signal and then retransmit the signal. The below diagram shows the working of the repeater, in which one user wants to communicate to a user working in segment 2.
02):- Hub
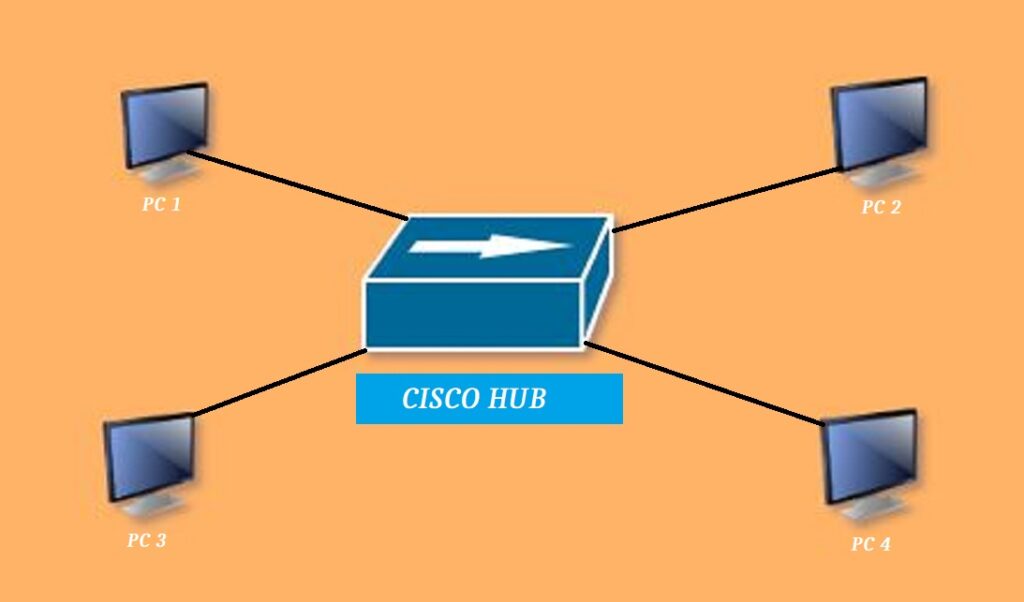
A hub is a centralized computer networking device. we connect our computers, servers and printers to it. it makes a star topology. A hub is a multiport ethernet device. we connect devices to it in LAN for resource sharing.It is working at layer 1. It is a multi-port device that amplifies a signal. The hub consists of multiple ports. That’s why we call it multi-port repeater. Every port of a hub works as a repeater.
Working of Hub
The hub repeats all the receiving information and broadcasts it to all nodes connected to it. Broadcast creates unwanted, unnecessary traffic, which finally creates congestion in the network. The congestion happened because the hub didn’t have enough memory to store the addresses of the devices. That’s why it forwarded all the data coming from the back.
Types of Hub
Active Hub
Passive hub
Intelligent Hub
Active Hub
A Central connecting device in a computer networking device that regenerates the signal on the output side to keep the signal strong. Active hub requires electrical power.
Passive Hub
The passive hub forwards the signal coming from the back. It doesn’t amplify or purify the signal, but just forwards it. It doesn’t require any electricity.
Intelligent Hub
It doesn’t only reconstruct or purify the signal, but also monitors the traffic going across its ports. It is a manageable device. The administrator can configure every port for monitoring purposes. We also call it a manageable hub.
03):- Bridge
The bridge is an important type of computer networking device that connects multiple networking segments. The bridge also filters data traffic in a network on the basis of MAC address. That’s why it works at the data link layer or layer 2 of the OSI model. A network bridge divides the network into different segments to reduce the amount of data traffic.
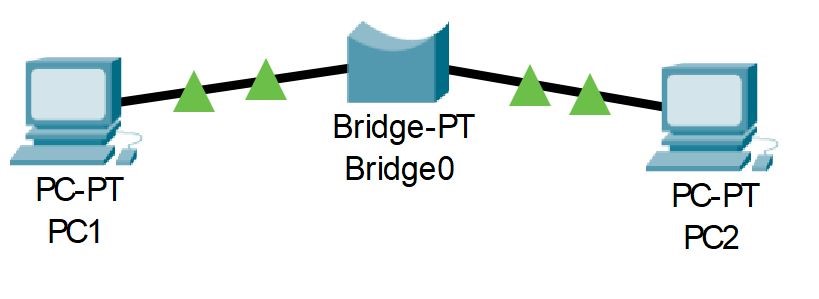
Working of Bridge
When data comes to the bridge, it will inspect the data by comparing the data with the forwarding table stored in its Mac table. If the data match with its destination mac address table, then the data will be sent to the destination, otherwise, it will drop the data.
04):- Networking Switch
A network switch is a device that connects different computer networking nodes. We also call it a multiport network bridge. The network switch works at Layer 2. There are other switches that work at Layer 3 and Layer 4, that’s switches are often referred to as Layer 3 switches or multi-layer switches. These switches can act as a router. The switch receives a message from any device connected to it and then transmits it to the required destination. As hub broadcasts, every message to its connected devices every time, but the working of the switch is different from the hub. It only sends the message for which it has been sent. Switch broadcasts the message only when the destination address is not listed in its MAC table.
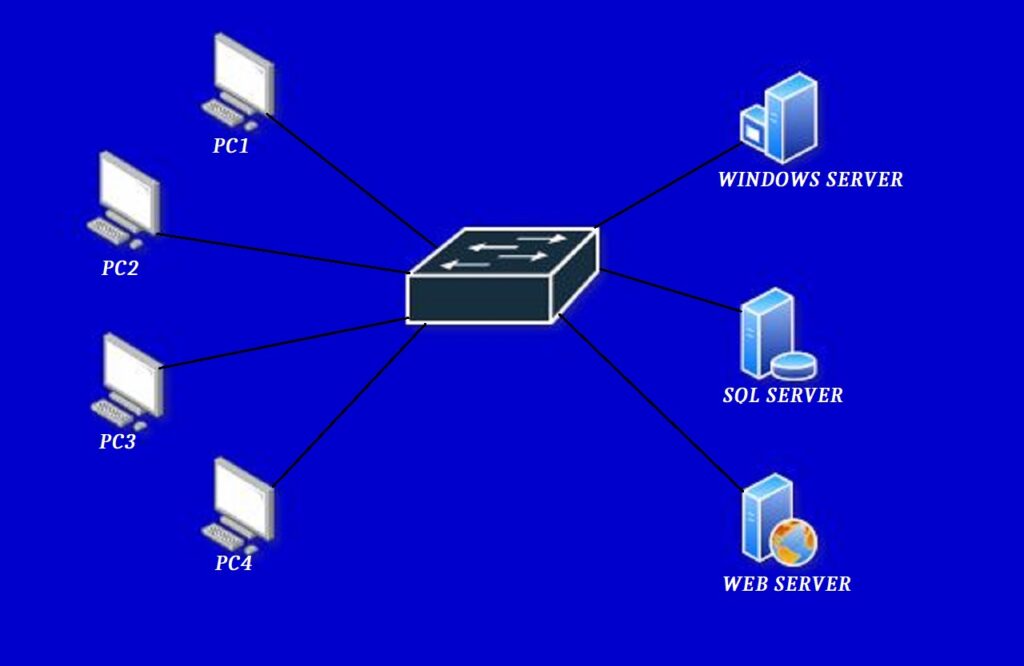
Working of a switch or how switch builds MAC address Table
The network switch uses a MAC address table or a Mac Table. The switch uses this table to forward data traffic from one port to another port. When we power on the switch for the first time, then this Mac address table is empty. The switch makes a Mac address table on the basis of the source Mac address of its connected devices. When PC A sends a message to PC D, then 1st frame will go to switch, as there is no entry in the Mac table. So the switch will start to broadcast the frame, and that frame will be received by every PC but only PC D will reply to the frame because the frame is sent to the PC D. As the switch gets the reply, the switch learns its mac address and store its entry in the mac table.
Similarly, when PC B sends a message to PC C, as by receiving a request from PC B, the switch will also learn PC B’s MAC address through PC B’s source MAC address, and As there is no entry of PC 3 Mac address in the switch mac table, so switch will broadcast the message sent by PC B, Every PC connected to Switch will receive that broadcast except PC B because PC B port is source port. As the message has been sent for PC C, only PC C will reply to the switch and all other PCs will just drop the message.
So switch will learn and store its Mac address in the Mac table by receiving a reply from PC C. In this way switch will build the Mac address table of its connected devices.
Types of Network Switch or switching
There are four forwarding mechanisms a switch can use.
- Store and forward
2) Cut through
3) Fragment-free frame
4) Adaptive switching
What is the difference between these types of switching?
i) Store and forward
In-store and forward switch, when a frame is received by switches then switch 1st waits to store the entire frame, and check in it any error. If any error in it then drop it. if there is no error in a frame, then switch and send it to the destination. This mechanism is slow but it is more reliable because it delivers an error-free frame.
ii) Cut Through
In the cut-through mechanism, as the switch receives a frame, the switch checks it up to Mac hardware or Mac address and then sends it to the destination. As the switch gets its Mac address, then it starts to send the frame. In this mechanism, there is no checking of errors in a frame. This mechanism is the fastest type of switching. There is no guarantee that the frame is error-free because it doesn’t check frame error. It is the fastest type of switching. There may be an error in a frame that reaches the destination.
iii) Fragment-free frame
Fragment-free frame is a combination of store & forward and cut-through switching. It checks the frame up to 64-bit where address information is stored and then delivers the message. Normally, It is seen that the collision domain is found up to 1st 64-bit, that’s why it checks 1st 64-bit. If there is any corruption in a frame, then the switch blocks that frame.
iv) Adaptive switching
In this method of switching, the switch selects any of the above three modes according to the situation.
Conclusion
Now a day’s most switches use the store & forward mechanisms. The other methods are fast but they are compromised with error. The other three mechanisms increase the switch performance but don’t guarantee with error-free frame.
05):- Router
A router is a computer networking device that connects two or more than two networks. That’s why we also call it an Internetworking device which means, connecting more than one network or network of networks. A router has an OS that moves data from one network to another network. The word router is derived from the word “Route”, which means that a router moves data on the basis of its OS (ios) from one place to another place. For this purpose, the router creates a routing table, and with the help of the routing table, it moves data from one place to another place.
The router works at layer 3 of the osi model
Functions of a Router
• To connect different networks together
• It controls broadcast traffic
Several companies that make routers are CISCO, 3COM, HP, JUNIPER, NORTEL, HUAWEI
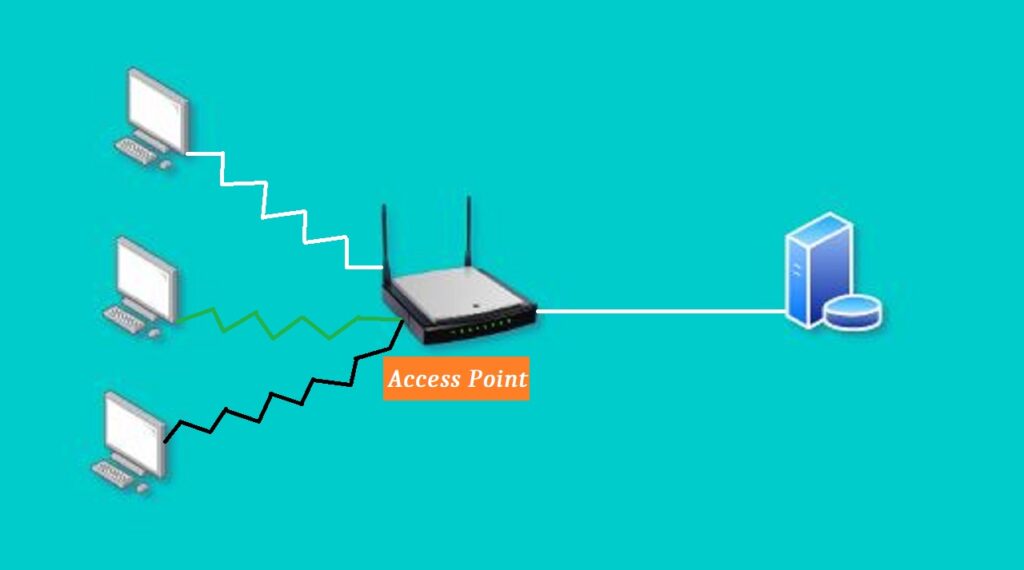
06):- Access Point
The access point is a computer networking device that connects other networking devices wirelessly to the wired network. Through the access point, we can make a local network as a wireless local area network or WLAN. we connect our personal devices like smartphones, laptops, and other organizational mobility devices to an existing network. A.P enables us to move portable devices from one place to another place. it works at layer 1 and layer 2 of the osi model and bridges wireless traffic to a wired network.
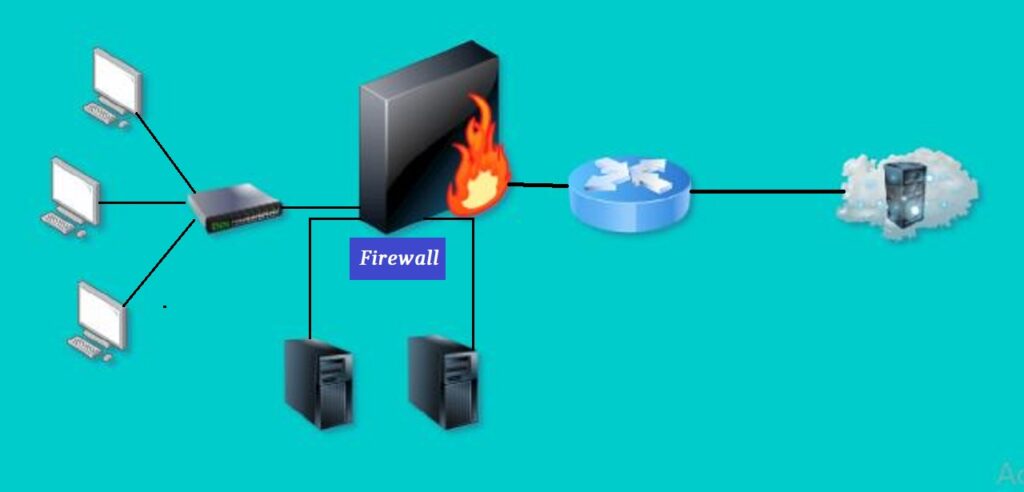
07):- Firewall
A firewall is a networking security device that blocks malicious packets from entering from an outside network (public network) to an internal network (private network). Firewall protects our private network from malicious activity, hacker, or unwanted software activity that harm our network. By installing a firewall in a network, it secures the network.
• There are two types of firewall
i) Hardware firewall e.g. ASA firewall, Palo Alto firewall, Citrix firewall, juniper firewall, etc.
ii) Software firewall e.g. Windows firewall, Threat Management Gateway, etc.